For years, the VET Coordinator’s role was often reduced to a logistical scramble: find a host, sign the paperwork, and get the student out the door.
But looking toward the 2026 academic year, the landscape for VET in Schools has fundamentally changed. With the Australian Government prioritising vocational pathways to address the National Skills Shortage, particularly in Aged Care and Disability, schools are now the frontline pipeline for the country's essential workforce. For Coordinators, this shift brings new pressure. It is no longer enough to simply find a spot. The new mandate is Workplace Learning Quality.
The scrutiny on Registered Training Organisations (RTOs) and schools has intensified. A placement is no longer just a box-ticking exercise; it must be a verified skill-building opportunity. For 2026, the question is not only: Is the student placed? It is: Is the student learning, safe, and gathering valid evidence?
This guide outlines the framework for managing high-growth VET Delivered to Secondary Students (VETDSS) programs without drowning in administration.
Fast Facts: VET in Schools 2026 Definitions
- VETDSS: Vocational Education and Training Delivered to Secondary Students. The nationally recognised term for VET programs undertaken by high school students.
- SWL (Structured Workplace Learning): Mandatory placement hours that contribute directly to VCE/VCAL units (specifically in Victoria).
- SBAT (School-Based Apprenticeship): A combination of paid work, school studies, and vocational training that is seeing double-digit growth in Queensland.
- Evidence Validity: The requirement under ASQA Standards is that logbook evidence must be verified as authentic, current, and sufficient.
The High-Stakes Sector: Validating Aged Care & Disability Placements
Nowhere is the demand for quality higher than in the Certificate III in Individual Support (CHC33021).
There is no denying the massive shift towards Care qualifications for 2026. But let’s be realistic: managing an aged care placement is different compared to standard work experience. You aren't sending a student to the local shops to pack bags. You are sending them into a working health facility.
The 120-Hour Challenge
The CHC33021 training package mandates a minimum of 120 hours of work placement. For a Coordinator managing 30+ students, that is over 3,600 hours of risk, logistics, and evidence collection to oversee.
The challenge here is suitability. A local nursing home might be willing to take a student, but do they have the capacity to mentor them?
- The Old Way: Send the student with a paper logbook and hope for the best.
- The 2026 Way: Verify the host’s capacity before the placement begins and track the student’s daily progress digitally.
If a facility is understaffed, your student might be left unsupervised or relegated to making tea for residents. Without visibility, you won't know this until the placement is over. SkilTrak acts as the transparency layer, allowing coordinators to see daily log entries and ensure the host facility is providing a safe environment that meets training package requirements.
Need help managing high-risk placements? Explore our Managed Services packages, where we handle the vetting for you.
Ensuring Training Alignment: The Quality Experience Factor
One of the most frequent concerns we hear from RTO Managers is the ‘menial task’ trap.
Imagine a student enrolled in Certificate II in Cookery placed at a hotel. Three weeks later, you discover they have spent every shift washing dishes. They haven't learned the required skills.
This is a quality failure. While the student was at work, they were not in training.
How to Fix Training Alignment: Proactive Alignment & Visibility
Ensuring a quality placement starts before the student arrives on site. SkilTrak facilitates the upfront process of aligning the student with an industry host and ensuring expectations regarding the training plan are clear to all parties.
Once the placement begins, you cannot physically be on-site daily to monitor the quality of training. However, SkilTrak’s digital logbooks provide the necessary transparency layer. Instead of waiting until the end of the term to discover a quality issue through retrospective paper logs, the digital evidence trail gives Coordinators visibility into the student's reported activities.
This data empowers the Coordinator with the information needed to manage the placement effectively and ensure audit requirements are met.
Streamlining Evidence: The End of the Paper Chase
Let’s be clear: SkilTrak does not replace the RTO’s responsibility for compliance. The RTO is always the legal authority. However, we facilitate VET Evidence Collection by ensuring the data you capture creates a Digital Evidence Trail.
Why Paper Logbooks Compromise Audit Readiness
The Friday afternoon panic is a ritual in too many schools: chasing students for wet, torn, or unsigned logbooks before the term ends.
- The Risk: A paper logbook can be signed retrospectively. A student can fill in 20 hours of shifts they never worked, and a busy supervisor might sign it without checking.
- The Result: Invalid evidence. If an auditor checks the roster against the logbook and they don't match, the student’s competency is at risk.
Real-Time Assessment Evidence:
To protect the integrity of the qualification, schools are moving to real-time evidence.
- GPS & Timestamps: Students clock in/out on their mobile. We provide the data point of exactly when and where they were.
- Supervisor Verification: CRM approves shifts digitally on their own device.
- Secure Storage: No lost books. The data is stored on the platform, ready for the training provider to evaluate instantly for an ASQA or state-funding audit.

State-Specific Requirements: Adapting to Local Rules
Australia does not have a ‘one size fits all’ system. A Coordinator in Parramatta faces different rules than one in Geelong. Your management system must speak the local language.
- Victoria (VRQA & SWL): Structured Workplace Learning (SWL) in Victoria is subject to stringent regulations. SkilTrak helps Victorian schools map placements to VCE outcomes.
- NSW (NESA & EVET): For NSW schools, managing EVET courses involves rigorous ‘Duty of Care’ checks. SkilTrak streamlines the collection of mandatory HSE checks.
- Western Australia (WACE): Meeting WACE VET requirements necessitates strict recording of hours to ensure credit points are allocated toward graduation.
- Queensland & SA (QCE & SACE): Every hour counts. A lost logbook isn't just an admin annoyance; it is a potential loss of credit points.
Future Trends: The Role of AI in 2026
While mastering current compliance is critical, forward-thinking Coordinators are also looking at how technology will shape the next academic year.
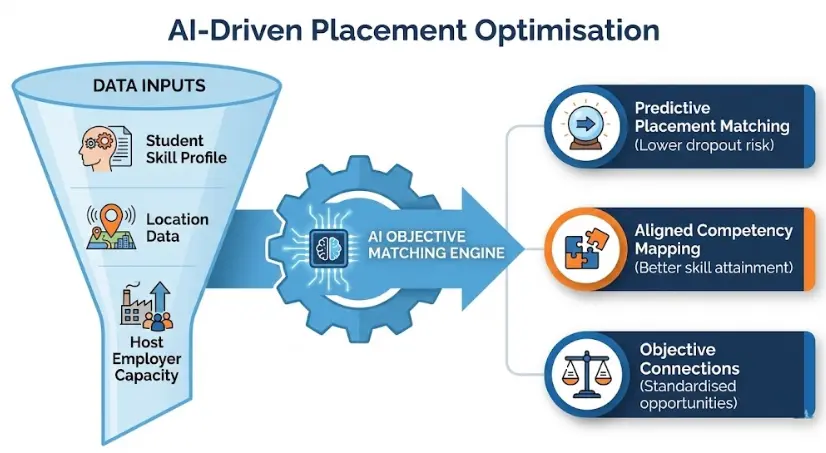
With the rollout of the National Framework for Generative AI in Schools, RTOs must prepare for a future where placement matching is data-driven. Currently, purely manual selection can lead to inconsistent outcomes.
By 2026, we anticipate Objective Matching will become standard. AI tools will analyse a student’s skills profile, location, and transport options to suggest the optimal host employer. SkilTrak facilitates this through:
- Predictive Placement Matching: Using historical data to suggest placements where students are least likely to drop out.
- Skill Gap Analysis: Automatically identifying which competencies a student is missing based on their logbook entries.
Read more about our vision for AI-Driven Vocational Training.
Conclusion: The Quality First Approach
The days of manual spreadsheets and ‘hoping for the best’ are over. With complex qualifications like CHC33021, the jobs market is desperate for qualified staff, not just students who have ticked a box.
As a Coordinator, your role is to establish the link between the classroom and the workplace. At SkilTrak, our role is to make sure that link is strong, clear, and visible.
